You can use alternative methods to start a session. The keyboard shortcut ‘Ctrl + N’ and the ‘New’ icon on the main toolbar also bring up the ‘New Monitoring session’ screen.
The ability to analyze and monitor COM port data is important when working with serial devices. Insight into the data traveling through your system’s RS232/422/485 ports can be instrumental when installing new equipment or troubleshooting network problems. You can monitor serial data to view event messages sent from applications and the status of serial devices.
The Windows operating system does not have any native facility for serial monitoring. You can, however, use specialized communication software to monitor serial ports and analyze your computer's serial activity. We are going to show you an excellent software tool that enables you to monitor serial port traffic in Windows.

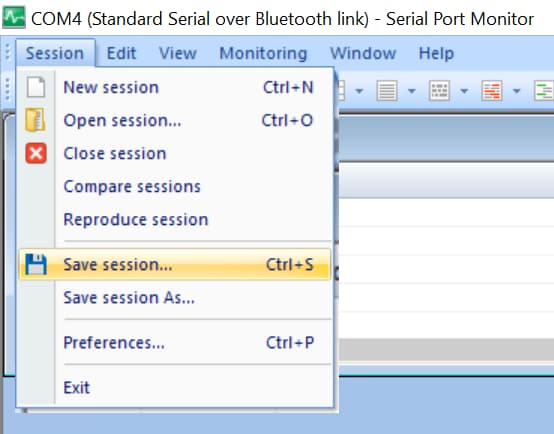
When saving your session give it a meaningful name so you can easily identify it for later analysis.
Sometimes you may run into a situation where it can be very beneficial to have a method that allows you to monitor the RS485 and RS232 data from multiple serial devices at the same time. One scenario that definitely falls into this category can occur during testing for a new installation of a number of serial monitoring devices. There seems to be a problem as while monitoring serial ports you discover inconsistencies in the data being produced by the devices.
Having the ability to monitor the serial port communications of all newly installed devices can help identify and resolve the issue in a timely manner. This is just one example of the utility that can be gained by having your team monitor COM port device communication for several devices simultaneously.
Electronic Team’s RS232 Port Analyzer is an excellent serial port monitor for Windows 10 that lets you easily perform a comparison of several previously saved sessions to discern any differences. Lean more how to add serial port in Windows 10.
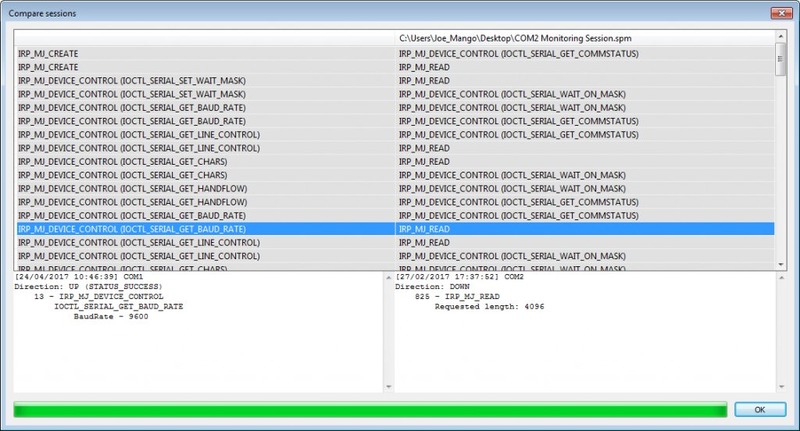
Reproducing the flow of data of a prior transmission between a port and a device or application can be instrumental in enabling you to troubleshoot problems in your serial network. Making incremental changes and testing the response when the same data is sent can help pinpoint the issue and lead to a quick resolution.
Serial Port Analyzer offers a simple method with which to accomplish this type of comparison by letting you replicate the data sent in a previous monitoring session. Transmitting this data to the port in question allows you to see if your actions have improved the situation.

Observing a computer system’s flow of serial data is a difficult task to approach without the use of a serial monitoring tool. The addition of a monitoring application to your software toolbox lets you easily get a picture of the data transmissions between serial ports and devices. You can monitor RS232 data as well as display, analyze, and log the data. A tool with these benefits will appeal to developers in many situations. Here are a few of them:
✅ Monitoring multiple serial ports simultaneously can be a very important feature of COM monitoring software. You can obtain a more complete picture of your system’s serial device interactions when you can view them at the same time. You also save valuable time by not having to individually monitor each port or device. Learn more about how to test serial port communications in the simplest and most efficient way.
✅ Hardware COM monitoring solutions are prone to experiencing latency and time-lag problems. This can complicate a developer’s ability to successfully monitor and debug their systems. A software solution can help reduce these issues, streamlining development efforts.
Features such as a user-friendly interface that displays the monitored data in a variety of formats streamline the monitoring process. You can save data in files and use them at a later point for more analysis and the transmissions and connections are time-stamped for easy review and comparison.
✅ A software implementation of a COM monitor means you don’t require extra cables to monitor RS232 ports. There are hardware RS232 sniffers which allow you to monitor your serial communication but they will require the use of additional cabling in order to function correctly.
Extra cables mean more time spent managing the cables as well as the initial expense in purchasing them. Ease of use and reduced costs make an application like Electronic Team, Inc. Serial Port Monitor a better choice than a hardware serial monitor.
✅ Substantial time and financial savings can be enjoyed by your IT team by using a software serial port monitor. Money is saved by not purchasing additional cables or hardware monitoring equipment.
Many businesses in industries as diverse as communications, design services, and semiconductor manufacturing have improved their bottom line by employing serial monitoring software. Its use can help smaller companies perform reverse engineering and gain a competitive edge on their larger counterparts.
Using a serial port analyzer can produce benefits for many businesses. In today’s competitive market, any small process improvement can lead to an advantage over a company’s competitors. The choice between a software and hardware solution to monitoring your serial communication is an easy one. The software application is much more flexible and cost-efficient.
✅ Operating a software serial monitoring solution does not require any specialized programming skills. You just need basic computer skills that enable you to install and launch the software tool on your system. Once that is done, any authorized user can easily monitor, log, and analyze all of the serial communication occurring between your system’s COM interfaces and devices.